I’ve given a few talks about my experience learning to teach. This is an edited version of my speaking notes for the keynote I gave at the Computer Science Teachers Association conference. This is the best distillation of my thoughts about the value of open source in my life, and what motivates me to contribute and teach. The first half is over 2000 words, so I’m breaking this into two posts. The next part I publish will be the second half of the talk – about the classes I’ve taught, and my lessons learned about what people need to know to get started in free and open source software.
I am a beginner teacher. I’ve only just started writing lessons and teaching classes to adult women who are learning or practicing their programming. All of what I share today is based on my personal experiences working with first time, adult programmers. My plan today is to tell you a little bit about me and what motivates me to teach and contribute to open source, share with you the successes of some of our beginner adult programming efforts and finally what I think open source communities offer teachers.
And I want to start by giving away my punchline. When it comes to working with open source community – of which I’m a member and a leader, and there are many, many leaders without any kind of central authority – I can say for sure today that we’ll come to you.
I’ve been working for the past couple years to find like-minded open source community members, and for those of you in the audience today, I am making a commitment to you – if you want it – to find an open source person to come and talk about what it is that they do to your classroom.
Just contact me (you can leave a comment below – just indicate if you’d prefer I not make your comment public), and I will make this happen, either through Mozilla or through my open source collaborators. I’ve spent the last 16 years going to conferences, and I would like to introduce that network of people to you.
I want to start with something Julie Horvath said recently. She wrote a blog post about women in tech and it struck such a chord with me. The first sentence really stopped me dead in my tracks.
I didn’t grow up thinking I could do anything I wanted to.
When I look at this again, I feel overwhelmed by how much it matches what the women I’ve taught said that they think about programming.
I see this every time I walk into a classroom to teach beginning programmers. This is a photo from a class on algorithms, people doing a pen and pencil exercise in groups. Several women said afterward they finally felt confident that they could explain what algorithms were. That before coming and working on this in these groups, they literally had never really thought about how algorithms related to programming or what it might mean to implement or create their own algorithms.
I’ve come to think of this as a possibilities problem. People truly have no idea what is possible for them in computer science. And in my teaching experience in particular, many women coming to these classes have a very limited view of what they can accomplish. They don’t know what the job opportunities are, they don’t realize how programming can be used in their lives outside of work, and they know very little about how a computer works or what the main components of a computer are.
When I think about what I really need to do — what my focus is in teaching that I do — I think about changing the scope of what people think is possible. Broadening the scope, and enhancing whatever details I can that make studying programming and ultimately computer science relevant to the lives of the people coming to these classes.
So if we were to just to attach a little overdeveloped importance to this idea of expanding the scope of possibility, we could call this “possibility engineering.”
In my experience, there’s two basic things I have to do – I need to raise awareness, and then I need to offer encouragement. It’s in addition, of course, to teaching real skills that people need. And as classroom teachers, you’re all aware of the need for these two things. I’ve found that these issues are often left out of how outreach and teaching in open source communities is structured.
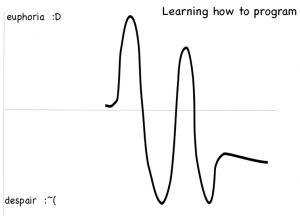
This is a picture of a sticky note I drew of how I felt while learning to use a new programming language or trying learn a new module in Python. The top of the graph is “euphoria” or “happiness”, and the bottom of the graph is “despair” or unhappiness. You can see I have a lot of ups and downs!
The peaks are when I’m reading documentation for the first time, succeeding with experiments and implementing code. The valleys are when I actually try the tutorials and they don’t completely work, when I write code that fails and when I’m trying to refactor my test suite. In the end, my emotions level out and if I’m lucky, I end up satisfied with the tool I chose to work with.
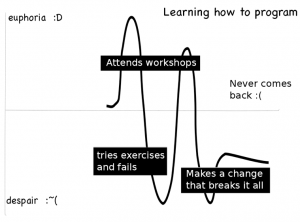
Here’s what I think happens sometimes with the women who come to PyLadies and then never come back. They initially are very happy, but then something happens that causes them to give up.
In one case, I know exactly what happened — a woman attended the workshops, tried things on their own that didn’t work, and then finally had something break with Python on her Windows laptop and she never came back.
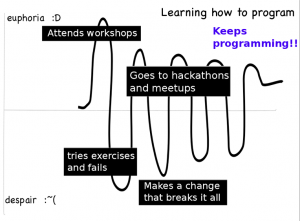
What happens when PyLadies succeeds? What does the emotional graph look like?
What I’ve seen in the 60+ women that keep coming to meetings is that they continue to have difficult experiences – things break, they don’t know how to fix them.
But they all come back to the group. They ask questions, they commiserate over things that don’t work and they get the help they need to see that they are improving at the same time as they feel as though they are getting better, making friends and being supported. The in-person experiences are key.
Before we go on, it’s important to acknowledge a key truth about what it is that teachers are teaching. Computer Science is a way of thinking and solving problems. It’s not a company or a product.
This is of course obvious to all of you in this room – but it’s such an important idea to come back to to in all of our work. It’s about getting kids or adults to understand the basics of what a computer is and what it does, and how it stores data about what, where, how and when we do things. We need people to understand these concepts in the same way that we need people to be able to read. When our society is increasingly assisted, augmented and controlled with the help of computers, democracy is at stake when most people have no idea how a computer and software works.
The role of open source groups like PyLadies, of non-profits like Mozilla, is ultimately to empower people: to spread knowledge, dispel myths and invite exploration.
But these groups are mostly helping out people who are already out of high school.
There’s a fair amount of research at this point about what many people think about computers when they’re in high school. I’ve mostly read about what girls think, and try to keep that in mind when I’m advertising my courses. Which brings me to what I thought computer science was all about when I was in high school.
What I knew was:
- Computers were for playing games
- Computers were for anti-social boys
- You’ll find lots of inappropriate, animated ASCII art on computers
And I think that highlights a problem with how we’re collectively handling explaining computer science to the world. We can’t rely on ad-hoc self-education, or discovery learning to help people understand how the whole world is changing.
Here’s a list of job titles from my colleagues in the industry. Many of these are jobs that didn’t exist 20 years ago, some are jobs that didn’t exist five years ago. So much is changing so fast.
Despite that, we have some real principles – computer science principles – underpinning it all. That’s where we need to focus, while at the same time exposing people to this wealth of possibility.
So, how did I, a person who thought the computers were for gaming, for boys and probably a little bit seedy, get from there to thinking it might be possible to join an open source community and move on to actually changing something I cared about?
In 2000, I made my first contribution to an open source project. I was working at Intel, managing network equipment monitoring and I’d found a problem with how I’d set everything up and needed to modify something like 7000 files to fix it. So I wrote a simple script.
Not too long after that, someone else had a similar problem and posted about it to a mailing list. So I decided, I might as well help that guy out and post the script. Then, I did.
And what happened next totally changed my life. The maintainer of the project not only thanked me, and asked a bunch of questions, he accepted my patch committed it to the main repo, and added me as a contributor to the project’s site.

I changed the source code of a tool I used every day.
I felt deliciously powerful, so important! And incredulous that something that I’d written that was so obviously terrible, was good enough to be part of a piece of software that I not only used every day, but thought was incredibly great.
And other people used it! I know because I got bug reports later.
Today, I’m a major contributor to the PostgreSQL community, and I founded a chapter of PyLadies in Portland. I’m also deeply involved in many aspects of open source community organizing, like running conferences and helping out with the Ada Initiative. It’s hard to understate how much that patch affected the rest of my life.
I’m super passionate about open source software and I really think collaborating with teachers is awesome. And what I think in particular is great about collaboration between us is getting the open source community to understand teaching at scale. By that, I mean learning how to teach everyone — the way that we teach in our public education system.
Public education is a grand experiment, and a very successful one. Despite the many issues we have with the administration of it, we have a literacy rate that enables us to sustain a democracy and a system for getting an incredible amount of information to most of our republic’s citizens.
We should be using this system to teach everyone about computer science.
Beyond that, I want open source communities to figure out how to teach at that kind of scale. Not only do we need computer science in the classrooms — we need free and open source principles and tools to be taught as well.
We can get there with community members reaching out to teachers as a first step.
And an important part of that is learning what the process of developing lessons and teaching students in classrooms is all about. This is the huge thing we (free and open source developers and community members) can learn from you (teachers).
Teachers and open source community have a lot in common. Some of the more important things are:
- Minimal resources
- Teach anyone who shows up
- Change the world by sharing ideas
My dream in this is that we’ll find a way to provide effective computer science education for everyone.
We’re trying to find that minimal set of concepts that will make people feel empowered at a keyboard, a kiosk or any computer they interact with in their lives. That they understand what’s being said in the newspaper about computers, that they can ask questions without feeling shamed or stupid, and that they can learn more if they choose.
And I don’t mean at all to say that you’re all signing up for teaching everyone. But I am signing up to at least try to do this for the adults in my life that need and want it.
Second half of this talk coming shortly…